COVID-19, Brief Review on epidemiology, prevention and anti-viral drug of Unani medicines
S. Nizamudeen *1, Huda Nafees 2,Muzafar Din Ahmad Bhat 3
1Department of Moalajat, Government Unani Medical College,Chennai, India.
2Department of Saidla ,Ajmalkhan tibia college , Aligarh ,India
3Department of Moalajat,National Institute of Unani Medicine, Bengaluru.India
- *Corresponding Author:
- S. Nizamudeen
Department of Moalajat, Government Unani Medical College,Chennai, India
Tel no: +91- 7010913469
E-mail: drnizamgumc@gmail.com
Received Date: August 24, 2021; Accepted Date: November 15, 2021; Published Date: November 25, 2021
Citation: Nizamudeen S, Nafees H, Ahmad Bhat MD (2021) COVID-19, Brief Review on epidemiology, prevention and anti-viral drug of Unani medicines. Med Clin Rev. Vol: 7 No: 10.
Abstract
WHO On 31st December 2019 informed, cluster of cases of pneumonia of unknown etiology from Wuhan, China, later named as COVID-19 now a global pandemic, with contagious all over the globe. The concern raises as more than 60% of the cases are asymptomatic/presymptomatic carries as these peoples are more prone to spread the infection and for symptomatic and infected persons the targeted treatment has yet to be developed. It has been testified that traditional remedies may alleviate the symptoms of COVID-19. Unani Medicine is one of the world’s ancient medical system that has many preventive regimes with treatment for many diseases including infectious fevers. However, a major hitch is a privation of precise scientific approach. Many studies of the Unani dugs has been proven for various immunomodualtory potential and antiviral against many viruses the potential compounds from these drugs also has been targeted against specific viral activity, this article aims to explore these Unani drugs as these drugs might have potential effect in prevention or treatment for COVID-19, its substantiation can take us for translational research to prove its scientific evidence on prevention and management of COVID-19.
Keywords
COVID-19; Unani Medicine; Antiviral; Translational research
Introduction
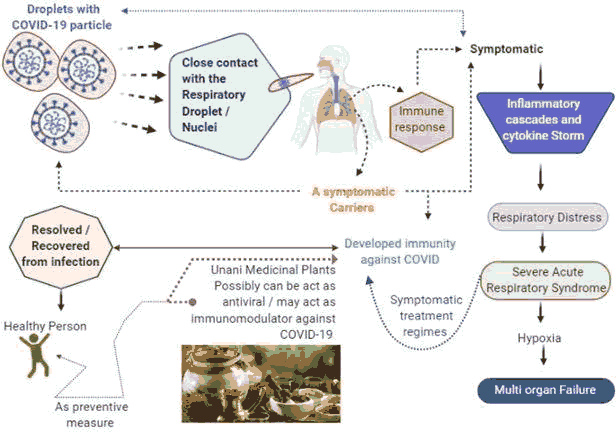
Emergence and re-emergence of epidemic and pandemics since time, has always been a threat to humans and livestock. In December 2019 few cases of pneumonia of unknown origin reported in Wuhan, china, raised a concern for emerging an outbreak and laboratory test confirmed as a new form of Corona virus [1-7]. On 11th of February 2020, WHO announced a new designation for epidemic disease: Corona virus disease (COVID-19) caused by 2019-nCoV. a RNA virus mimicking SARS with the different genome sequence. Since two decades the impact of emerging infectious disease has an average growth of 6.9 % annually. The out breaks of H1N1, SARS, Ebola, MERS and Zika has witnessed many deaths with raising earlier concern in spreadi+ng the infection and earlier management and reducing the risk and mortality rate [8-14]. It is swiftly spreading across many other countries as on dated april-16 2020, Covid-19 has affected more than 2 billion peoples with 44 lakh deaths around the globe. In India as on dated covid-19 has infected 3.2 crore with 4 lakh deaths. Even though china has taken measures with lockdown the fear of resurgence and third pandemic wave outbreak is a matter of concern COVID-19 pandemic has shook the world with massive economic plunge affecting daily economic activity over the globe Evidences determine for sustainable transmission of COVID-19 from animals to humans as this issues has been in a laydown to plunge the wet markets but the exact origin of the virus, continues to remain as a mystery, to the scientist around the globe. The previous corona virus pandemic has been reported for possible reservoir SARS-CoV from palm civet meat and MERS-CoV from bats /camel .The full length genomic sequence of COVID-19 is obtained and sequence discovered as 29,870 bp with a GC content of 37.99% to 38.02% and sequence placed as 50 -ORF1ab–S–E–M–N–30 which is phylogenetic ally similar to a bat SARS-like CoV with likeness of 87.6% to 87.7% these discoveries evidently put forward that bats are the intermediate host and now speeding from human to human [15-21].
Only treatments with HIV antiviral and chloroquine phosphate is established but the potent targeted antiviral drug or vaccine for COVID-19 is yet to be discovered, another major setback is the raise of asymptomatic carries, emerging pattern propose that between 5% - 80% of people testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 may be asymptomatic of CoV and these asymptomatic become symptomatic in next subsequent week and the whole population cannot be screened for as there is no such reliable policy yet available as the disease is spreading instantly without any room for development of new policies and drugs [22-28].
As since the human race use of medicinal plants been a traditional way in prevention and treatment of many diseases , Unani medicine has its deep root in the development of modern medicine in many ways and this system has been widely accepted over the globe, according to world health organization 80% of world’s population uses medicinal plants in a single or in combination for different ailments and for preventive measures or as tradition in specific countries with substantial usage of traditional medicinal plants as like China is one of the most sponsored country in exploring medicinal plants for the modern drug discovery from phytochemicals. Improved separation technologies offer potential screening of medicinal plants a very wide opportunity for laying drug pipeline discovery .Unani system of medicine is one such traditional system of being practiced since 2500 years, which has treasures of medicine plants and its usage in variety of ailments. Govt of India has approved clinical trials in inter-disciplinary approach though herbal remedies and also one clinical trial has registered to see the efficacy of Unani compound drug, considering the exponential growth with increased mortality in second wave it is very necessary to prevent the tremendous spread of this disease by improving preventive measures and by increasing the innate immunity to combat the disease, Unani medicine can work tremendously in increasing individuals immune system in this pandemic outbreak.Few clinical trials in china, with usage of herbal drugs in moderate and severe cases have shown less mortality and speedy recovery. In India integrated approach with AYUSH system of medicines and allopathic medicine is still seems to be a parallel way of approach, the scientific evidence to each and every herbal drug is highly complex. Many Invtitro , Invivo and Insilico studies of the Unani dugs has been proven for various immunomodualtory potential and antiviral against many viruses the potential compounds from these drugs also has been targeted against specific viral activity this article aims to explore these Unani drugs as these drugs might have potential effect in prevention or treatment for COVID-19 Unani literature provides diet regime, treatment with drugs in pandemic diseases and these prescribed single, compound drugs has shown to be effective in many types of choric fevers [29-35]. Greek physicians of time have established the importance of disease prevention and control. Hippocrates , in the commentaries on book of epidemics, has given the detailed description of “Infection Prevention, control and Treatment of Epidemics” other physicians Avicenna and Galen has stated the cause of epidemic to be caused by contaminated air which is contagious to spread infection, Hippocrates is the first person to introduce practicing of quarantine [36-42].
Etiology
Caused by SARS-CoV 2 (2019-nCoV) that belongs to coronaviridae family [43-49]. Coronaviruses are a large group of enveloped viruses of diameter 60 to 140 nm, non-segmented positive sense single stranded RNA viruses associated with a nucleoprotein within a capsid comprised of matrix protein. It has 39 species under the kingdom Riboviria, belonging to the family Coronaviridae, suborder Cornidovirineae and order Nidovirales. Coronaviruses are divided into four genera: α, β, γ and δ coronaviruses. The most genera transmission from animal to human is α, β CoV, the SARS-CoV comes under the species of severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus and genus β-coronavirus [50-56]. Most of the species are enzootic and currently only a few among them infect humans. Till now seven human CoVs (HCoVs) have been con-firmed. precisely, α-coronavirus genus named as Human coronavirus NL63 (HCoV-NL63) and Human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E), β-corona virus genus named as Human coronavirusOC43 (HCoV-OC43), Human coronavirus (HCoV-HKU1), SARS-CoV,SARS-CoV-2 and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus(MERS-CoV), coronavirus strains HCoV-229E, HCoV-NL63, HCoV-HKU1 and HCoV-OC43 cause mild respiratory diseases in humans. Whereas SARS-CoV-2 is a zoonotic virus that belongs to the Coronaviridae family that can infect several animal species and human. The raise of asymptomatic carries is a concern and emerging pattern propose that 2% of the population are asymptomatic carriers of a CoV , about 5% to 10% of the population reported for acute respiratory infections [57-63].
Epidemiology
COVID-19 outbreak is mesmerizing it is swiftly spreading across many other countries as of GMT+5:30 pm CEST, 23 Aug 2021, there have been2, 11,730035 confirmed casesof COVID-19, including4430697deaths,reported to WHO. In India as of 17:00 GMT+5:30, 23 Aug 2021, there have been 32449306 confirmed cases including 4, 35,110 deaths. With highest confirmed cases in Maharashtra (16758), followed by Gujarat (6625), New Delhi (5532), MP (3138), Rajasthan (3317), Tamilnadu (4829) and Uttar Pradesh (2998) Even though globally measures have taken with lockdown the fear of resurgence and second pandemic wave outbreak is a matter of concern, In India even after major lock down the cases are raising and booming up and many prevention and control programmes are being set up by Ministry of health and family welfare.
Modes of Transmission
COVID-19 is considered to be zoonotic with possible transmission to human from bats, wild animals by means of respiratory droplets from cough or sneezing in close contact with infected people. Form the first reported cases of pandemic the suggested animal to human transmission is form the Wuhan city, Huanan seafood market, Hubei province, China. On the other hand, the cases testified among medical staff with no history of exposure to Huanan seafood market or visiting considered for human-to-human transmission or cluster transmission from humans.
The scientific brief by WHO on 27 March 2020for modes of transmission defined three main routes of transmission for the COVID-19 a) Droplets transmission, b) Contact transmission, and c) Aerosol transmission. When an infected person coughs or sneezes droplets are ingested or inhaled when a person is in close contact within 1 m , Droplets of different size particles from >5-10 μm diameter is mentioned as respiratory droplet if it is lesser than <5μm in diameter is mentioned as droplet nuclei. Contact transmission may occur when a person touches a contaminated surface or object and consequently touch their mouth, nose, or eye. In a quite closed environment aerosol transmission possibly will occur, once respiratory droplets mix into the air, it can transfer through inhalation. Apart from these three routes one study suggested that, digestive system as a potential transmission route for COVID-19 infection.
Incubation and contagious period
The incubation period variable, based on current epidemiological analysis, the incubation period is one to 14 days, mostly from 3 to 7 days, with a maximum of 14 days. A study reported that 97.5% of persons infected with COVID-19 may develop symptoms within 11.5 days Covid-19 is communicable and can spread during the latency period.
Clinical manifestation and diagnosis
Signs and symptoms
Clinical manifestation of COVID-19 is variable on clinical course that is reliant on host and organism factors. Most of the persons with COVID-19 will experience, fever, cough fatigue, Anorexia, dyspnea, Sputum production, sore throat, Myalgia’s but in few cases, anosmia and dysgeusia also has been reported.
Laboratory findings
Decrease in lymphocytes is the most common laboratory finding in 2019nCoV and is found in as many as 83% of hospitalized patients. Lymphopenia, neutrophilia, elevated Liver enzymes (serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels), elevated lactate dehydrogenase, increase in CRP, and high ferritin levels .Elevated D-dimer and lymphopenia have been closely associated with mortality. Among those patients admitted in ICU with increasing critical illness had elevated Procalcitonin and high plasma levels of inflammatory makers, suggestive of potential immune dysregulation. In all the patients with mild symptoms of suspected infection, or positive history of exposure to the infected person mandatorily has to perform PCR real- time fluorescence (RT-PCR) to detect the positive nucleic acid of SARS-CoV-2 in sputum, throat swabs, and secretions of the lower respiratory tract samples [64-70].
Radiographic evidence
Chest radiographs of patients with COVID-19 typically demonstrate bilateral air-space consolidation, though patients may have unremarkable chest radiographs early in the disease. CT-thorax imaging shows lesions mainly in subpleural region, along the bronchial vascular bundles , mostly multiple lesion are seen ≥ 3, occasionally single or double lesions are noticeable , the lesions seems to be patchy, large block, nodular, lumpy, honeycomb like or grid-like, cord-like, etc with mostly patchy opacity, a paving stones-like change mixed with ground glass density and interlobular septal thickening, consolidation and thickened bronchial wall, etc. in few cases pleural effusion and mediastinal lymphadenopathy is seen.
Asymptomatic carries and screening
The covid-19 pandemic continues to evolve and the virus is mongering the fear of transmission from asymptomatic carries as any of the screened persons are not having any of the symptoms, and the risk is increased among health care workers In a cluster case sample screening in Chennai, Tamilnadu spurs as 80% of the persons were positive for COVID-19 with no symptoms it urges the scientist for any kind of mutation or antigenic shift, or any specific genus has become less virulent has yet to be discovered.
Prevention and control
The measures to be taken during any epidemic and contagion has many lessons from the previous epidemics in history of medicine, Infection Prevention and control has been there since long time as many pandemics emerged varyingly since the time, Greek physicians of time has established the importance of prevention and control. Hippocrates, in the commentaries on book of epidemics, has given the detailed description of “Infection Prevention, control and Treatment of Epidemics” other physicians Avicenna and Galen has stated the cause of epidemic to be caused by contaminated air which is contagious to spread infection, Hippocrates is the first person to introduce practicing of quarantine. A Treatise on the Smallpox and Measles written by Rahzes describes in the fourth chapter about the management, prev mention and control of infection In 14th century physician Ibn Qayyim al-Jawziyyah in his text book al-?ibb al-Nabawi defined how the disease transmits through close contact with the infected person. The first Bimaristan (hospital) built by Umayyad Caliph Walid ibn ?Abd al-Malik in the year 707 in Damascus, has separate quarantine wards for leprosy patients so as to prevent contagion even many of the religious teachings guide us through preventing contagion by quarantine as the Holy Prophetsarecognized and addressed the significance of travel bans and quarantine in places if any place is being epidemic with any disease in order to alleviate the spread of infection. He said, “If you hear of an outbreak of plague in a land, do not enter it; and if the plague breaks out in a place while you are in it, do not leave that place.” What we are facing through a social distancing and quarantine for infected and suspected peoples is a challenging task in this era as the vaccine has yet to be invented. India is under lockdown since 24th of march is a big plunge to all the sectors, but this is the only measure to be adopted for the spread of contagion a study done by Singh, R. and Adhikari a mathematical model to measure the effect of social distancing revealed that 49 days lockdown is to be much effective in prevention of resurgence and community spread. World Health organization and (WHO) and CDC has laid many polices since the outbreak in Wuhan, china from Infection control management and methods for infectious diseases, Strategy for medical institutes to adopt isolation treatment and observation protocols to prevent and control the spread of the COVID-19 and to prevent nosocomial infection .Strategies for measures to be taken in handling COVID-19 were introduced these include isolation suspected cases, isolation of identification and follow-up of contacts, environmental disinfection, and use of personal protective equipment .For general public as many of the guides has been released which includes: Basic protective measures against the new coronavirus, How to cope with stress during 2019-nCoV outbreak, COVID-19: Pregnancy & breastfeeding, COVID-19 Home care , Protect yourself and others from getting sick, Be ready for coronavirus Ask WHO, Protection measures for persons who are in or have recently visited (past 14 days) areas where COVID-19 is spreading [71-77].
On 14th of April 2020 WHO released five Global strategic objectives remain as follows: To Mobilize all sectors and communities to ensure that every sector of government and society takes ownership of and participates in the response and in preventing cases through hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette and individual-level physical distancing
To Control sporadic cases and clusters and prevent community transmission by rapidly finding and isolating all cases, providing them with appropriate care, and tracing, quarantining, and supporting all contacts.
To suppress community transmission through context-appropriate infection prevention and control measures, population level physical distancing measures, and appropriate and proportionate restrictions on non-essential domestic and international travel.
To reduce mortality by providing appropriate clinical care for those affected by COVID-19, ensuring the continuity of essential health and social services, and protecting frontline workers and vulnerable populations [78-84].
To develop safe and effective vaccines and therapeutics that can be delivered at scale and that are accessible based on need.
Treatment
To date, there is no precise antiviral treatment has been established to be effective counter for COVID-19. Concerning patients infected with COVID-19, it has been suggested to apply applicable symptomatic treatment and supportive, few of the possible treatment regimens being treated symptomatically to patients who have been admitted to the hospital with COVID-19 in china, according to COVID-19 guidelines.
The IDSA guideline panel recommends Prevailing evidence supports currently suggested management strategies. Hhydroxychloroquine/chloroquine.
• hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine plus azithromycin
• Combination of lopinavir/ritonavir
• The use of corticosteroids
• Recommendation
• Tocilizumab
• Convalescent plasma
However all these treatment don’t have any direct evidence in proving benefits as most of the COVID-19 infected persons recovered with minimal harm to body, the use of corticosteroids in context to inflammation of lungs may reduce the inflammation but it increases the risk of immunosuppression, Use of chloroquine is shown good recovery in COVID-19 china but yet its mechanism has to exploded .Carefully designed RCTs and prospective outcome registries are needed to determine the dose, route, timing, and duration of such treatment on the prevention of clinical deterioration and to better understand the potential harms associated with its use. If a person is on a steroid (inhaled or systemic) for another indication (e.g., asthma), the steroid should be continued. World Health Organization (WHO) has started their SOLIDARITY trial for treatment and valuation of various drug candidates and for better understanding of COVID-19 through all sets of clinical and observational studies More than 70 countries are in hands on to the trials as on date’s 17.4.2020 960 trials has been registered in which 532 trails has been registered by China, there is only one study Max covid-19 study being registered from India as on dated 17th April 2020 it’s an observational study. Three preventive study has been registered one is for adeno virus vector for covid-19 remaining two studies are being registered to prepare a protocol and clinical trial on Chinese medicine Gu-Biao Jie-Du-Ling in Preventing of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (COVID-19) in Children .reaming studies has been registered under different phases of trial in which 46 trials has been registered with the use of TCM in COVID-19. This is the era of scientific acceptance towards preventive and as well as treatment measure to be rolled out for fighting with pandemics ,even though human history has very wide use of herbs but science to explore the wide range of herbs in many disease yet a night mare ,resurgence of epidemics and pandemics takes us to search of medicine from the natural recourses as many of the medicinal plants has been proven for their immmunomodulatory and antiviral or adaptive mechanism for viral resistance mechanism and antioxidant activities etc and these medicinal plants are the main resources of Unani and other traditional system of medicine since many thousands of years , as this itself suggest for the friendly nature of natural herbs to adopt human body there by combating many different ailments , as well can be used as nutraceutical completed validation of these herbs is an need of an hour . And many of the medicinal plants having the antiviral properties can be prevailing the possible antiviral effects through inhibition of virus in at least one step of its propagation, completely inhibiting the virus without affecting the host cells, or any antiviral must have a broad range of activity and any antiviral must not be immunosuppressive Unani medicine has wide range of medicinal plants possessing antiviral properties all these drugs might be helpful in targeting the antiviral property for COVID-19. Many of the potential Unani herbs those have been proven for its antiviral activities against many viruses through Invitro, Invivo, Insilico studies as detailed in and few drugs has been proven for Sars-cov like Allium sativum Andrographis Paniculata, Glycyrrhiza glabra , Curcuma longa among which Andrographis paniulata and , Glycyrrhiza glabra might be the potential candidate. Few studies on compounds from medicinal plants like Terpenoids and Lignoids ,M. Betulinic acid , savinin , curcumin , and niclosamide f ,betulinic acid and savinin , α-cadinol has shown to be effective against SARS-CoV . Today computational biology has big role in modulating herbal drug target against many disease causative agents through bio-informatics and network pharmacology , few Insilco studies through molecular docking have been substantiated to be good antiviral drug candidates against COVID-19 like Andrographis paniculata , Aloe vera , Withania somenifera, Vitex trifolia, Syngium aromaticum and Tinospora cardifolia etc has shown good affinity to bind with COVID-19 spike proteins and specific aminoacid residues. Medicinal Plants are vital source of many active metabolites, and is essential for drug development. Capitalizing in exploration of ethno-medicine will be a way forward in protecting the global population from present and impending pandemics [85-94].
Conclusions
This review article is aimed to explore the current status of epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis with prevention control in preview with the Unani medicine preventive measures The persons who developed immunity for COVID-19 from asymptomatic serologically positive sate of infection or having recovered completely from symptomatic state of infection are likely to become the utmost reserve for any arrival of second wave of pandemic. All these patients are actually has to be sustained for their immune precisely, and monitored as the vaccine is yet to be discovered and this strategy can be managed by taking prophylactic measures in these patients after their convalescence period so the resurgence of outbreak can be prevented. Holistic approach will be an good measure in hands on with the combating the pandemic disease and to bring the towards promising treatment measures through Unani system of medicine and the medicinal plants can be as a whole or in combination with modern drug regimens or in preventive measure, the way to explore these medicinal plant is the need of an hour.
List of Unani antiviral drug studies
| In Vitro studies | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Botanical Name | Unani name | Metabolite | Mode of action | Target virus | Reference |
| Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees | Kalmegh | andrographolide, 14-deoxy-11,12-didehy droandrographolide, andrograpanin, 14-deoxyandrograph olide, (±)-5-hydroxy-7, 8-dimethoxy flavanone | Inhibition of the growth of HIV | HIV, HSV-1 , EBV, H1N1 Simian Retro Virus | (37) ((38)(39) |
| Syzygium aromaticum (L.) Merrill | Qaranfal | Eugenol | Inhibition | Hsv-1 , Hsv-2,Adenovirus-6, Poliovirus, and Measles, | (40) (41) |
| Eucalyptus globulus Labill | Kaphur | tereticornate A, grandinol, sideroxylin , Cypellocarpin C , litseagermacrane | Inhibition | HSV1, HSV-2 Influenza virus A2 | (42) (43) |
| Melissa officinalis L. | Badarendja-bouya | Phenolic compounds (Zcitral, geraniol, (Z)-nerol, germacrene-D, nerol, inalool, citronellal and citronellol.) | Inhibitory effect on virus replication | Hsv1, Hsv-2, Influenza A & BNewcastle disease, Mumps & Parainfluenza viruses 1, 2 , Avian influenza A virus (H9N2),Adeno virus | (44)(45) (46)(47) |
| Azadirachta indica A. Juss. | Neem | Polysaccharides sulfonoquinovosyldiacylglyceride | virus inhibition assay showed inhibition in dose dependent manner | Coxsackievirus B, Poliovirus Dengue virus type-2 HSV-1 and HSV-2 | (48) ((49)(50)(51) |
| N Terminalia chebula Retz. or T. chebula Retz. var. tomentella Kurt. | Halela Kabuli | chebulagic and chebulinic acids | Dose dependent potent in vitro direct anti-viral activity against HSV-2 | HSV 1 , HIV-1 | (40) (52) (53) |
| Punica granatum L. (Lythraceae) | Anar | Tannis | Inhibits HSV-2 replication, but also shows stronger effects of killing virus and blocking its absorption to cells. | Herpes type 2 | -54 |
| Achillea millefolium L. | Biranjasif, | Plant extract | Inhibitory activity on HIV-1 reverse transcriptase | HIV-1 t tickborne viral encephalitis | (55)(56) |
| Momordica charantia L. | Karela | Plant extract | Inhibition | HIV type 1 (HIV-1) | (57)(58) |
| Acacia nilotica | Aqaaqia, Babuul | Plant extract | Inhibition | HIV-PRHep C | (59)(60) |
| Allium sativum | Lehsun | Plant lectins,ajoene , allicin, allyl methyl thiosulfinate, methyl allyl thiosulfinate | Proteolytic and hemagglutinating activity and viral replication | SARS | (61)(62) |
| Andrographis | Kalmegh | Andrographolide , | Suppression Target (NLRP3, capase-1, | SARS-COV and likely | (63) (64) |
| Paniculata | entâÃâ¬ÃÂlabdene diterpenes | and IL-1β) | SARS-CoV-2 | ||
| Glycyrrhiza glabra | Aslussoos Mulethi | GlycyrrhizinSNMC, Diprenyl bybenzyl | Inhibition of viral replication, Modulation of membrane fluidity,Affects cellular signaling pathways, upregulate expression of inducible nitrous oxide synthase and production of nitrous oxide in macrophages.Inhibit SARS-CoV replicationIntroduction of 2-acetamido-beta-Dglucopyranosylamine into the glycoside chain of glycyrrhizin produced a 10-Inhibitory effect on viral proliferationfold increase of the anti-SARS-CoV activity | SARS; HIV-1 , Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) ,, cytomegalo virus. SARS-CoVvaricella-zoster virus | (65) (66)(67) (68) (69) |
| Vitex negundo | Sambhalu or sephali | Plant extract | Inhibition of viral replication, | HIV-1,Chikungunya virus 9(Asian strain) | (70) (71) (72) |
| Vitex trifolia | Sambhalu | Plant extract | Inhibition of viral replication, | HIV-1 | -70 |
| Achyranthes aspera | Chirchita | Plant extract | HIV-1 strain | -73 | |
| Rosa centifolia | Gulab | Plant extract | HIV-1 strain | -73 | |
| Curcuma longa | Haldi | curcumin boron complexesCurcuminoidsCurcuminCurcumin | Inhibition of HIV-1 and HIV-2 proteasesInhibition of haemagglutination in influenza inhibitory effects on the neuraminidasesDecrease of HCV replication by suppressing the Akt-SREBP-1 pathway3CL Protease Activity | HIV-1 and HIV-2Influenza H1N1 and H9N2HCVSARS-CoV | -290 |
| Camellia sinensis | Chaai | Plant extract | Polyphenol WILL inhibitProtease inhibition | Coxsackie A9, B1, B2, B3, B4, and B6 viruses, Echo type 9 virus, herpes simplex virus, poliovirus III, vaccinia virus, and REO type 1 virus | (76)(76) (77) |
| Withania Somnifera | Asgand | Ashwagandhanolide,Withaferin AWithaferin D27- hydroxywithanolide | Protease inhibitors | Covid-19protease (6LU7) | -78 |
| Peganum harmala | Ispand lahori | Harmine | Inhibition of viral entry | HSV2 | (79) (80) |
| Melia azedarach (Chinaberry Tree) | Bakayan | Meliacine (Glycopeptide) | UN ----- | HSv-1 and 2 | (81) (82) (80) |
| Moringa oleifera (Moringa) | Shajna | Plant extract | Inhibition after viral attachment | HSV1 | (80) (83) |
| Syzygium aromaticum | Qaranfal | Plant extract | Inhibition after viral attachment | HSV1 | (80) (40) |
| Ferula assafoetida | Heeng | Umbelliferone, coumarin-sesquiterpene complexes e.g. asacoumarin A & asacoumarinB. | Inhibition after viral attachment | HSv1H1N1 | (84) (85) |
| Anisoon | lignin-carbohydrate | interfere with virus adsorption | Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and -2),human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) and measles virus. | -86 | |
| Pimpinella anisum | complexes (LCs) Scopoletin, umbelliferone, umbelliprenine, bergapten | to the host cell surface and directly inactivate viruses | |||
| Gymnema sylvestre R. Br | Gudmar | Plant extract | virus replication inhibition activity | mouse coronavirus (MCV)0, HBV ,HIV-1 RT | (87) (88) |
| Bergenia ligulata | Pakhanbed | Tannins | by blocking RNA and protein synthesis in a dose-dependent manner | Influenza | -89 |
| Phyllanthus amarus | Bhui-amla | Tannins | inhibited HIV-1 replication by inhibiting reverse transcriptase in a dose-dependent manner | HIV | -89 |
| Embelia ribes Burm. f. | Baobarang | Fruit extract | suppress the growth of infuenza virus | influenza virus | -90 |
Table: 1
| Invivo studies | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Botanical name | Unani name | Model used | Mode of action | Target virus | Reference | |
| Azadirachta indica Juss) | Neem | Mice | inhibition of the virus replication asconfirmed by the absence of Dengue related clinical symptoms in suckling miceand absence of virus specific 511 bp amplicon in RT-PCR | Dengue virus type-2 | (91) | |
| Glycyrrhiza glabra | Aslussoos, mulethi | Mice | The highly significant decrease in virus populations recommended a strongviricidal effect in test plant extract treated embryos. | Newcastle disease virus | (92) | |
| Humans | Glycyrrhizin inhibits HIV-1 and reducessymptoms | HIV | (66) | |||
| Humans | induced a significant reduction of serumliver enzymes and caused an improvement in liver histology | HBV HCV | (65) | |||
| Humans | In this clinical study the count of CD4lymphocytes and the CD4/CD8 ratio in asymptomatic carriers (AC) | HIV | (65) | |||
| Humans | HIV-positive hemophilia patients seemedto be effective in preventing the development of AIDS by raising the numberof CD4-positive T-lymphocytes | HIV | (65) | |||
| Vitex trifolia | Sambhalu | Murine | Reduction | SARS-COV | (93) | |
| Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees | Kalmegh | Humans | HIV - phase Idose-escalating clinical trialAndrographolide shown Significant rise in the mean CD4+ lymphocytelevel of HIV patients | HIV | (94) | |
| Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn., | Akùb | Humans | In patients improved liver function | HBV | (95) (96) | |
| Psidium guajava L. | Amrud | Humans | The treatment with PG has good curativeeffect on infantile rotaviral enteritis. | Rotavirus | (97) | |
| Picrorhiza kurrooa Royle | Kutki kharbaqe-hindi | Rats | Reduced in symptoms with reduction inviral load and liver enzymes | Viral Hepatitis | (98) | |
Table: 2
| InSilico Studies | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Botanical Name | Unani name | Metabolite | Mode of action / Amino acid residues | Target virus | Reference | |
| Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.)Nees | Kalmegh | Andrographolide | potential to inhibit neuraminidaseactivity of H1N1 | H1N1 | (99) | |
| ASN 783, ASN 910 PHE 909, PHE 909, ASN 910,ASN 615 GLN 1028,SER 632 | Covid-19 | (100) | ||||
| Azadirachta indica A. Juss. | Neem | Deacetyl-3-cinnamoyl-azadirachtin | Potential inhibitor against NS3/4Aprotease. | HCV NS3 protease | (101) | |
| Syzygium aromaticum | Qaranfal | Carvacol Eugenol | ARG 637 TYR 311, SER 635, ILE 666 TYR 311, SER 635, ARG 637, SER 309, TYR311 | Covid-19 | (100) | |
| Tinospora cardifolia | Gilo | Cardiofoliolide B | PRO695, CYS697, GLN824,ARG700, ASN1091,PRO695, ILE1090, ASN1091,GLN824 | Covid-19 | (100) | |
| Aloe vera | Elwa | Aloe-emodin | 6LU7, ARG105, ILE106, GLN110, THR111, GLN178, VAL108 | Covid-19 | (102) | |
| Withania somenifera | Asgand | Withaferin A | 6LU7. PHE294, THR292, ASP295, ASP153,SER158, LYS102, PHE103, GLU178, ARG105, ILE106, GLN110,THR111, GLN178, VAL108 | Covid-19 | (102) | |
| Embelia ribes Burm. f. | Baobarang | Embelin | Glu190, Arg193, Ser227, and Gly228. Tyr98 and Val135 | Influenza Virus | (90) | |
Table: 3
| Antiviral compounds from plants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | Mode of action | Target virus | Reference | |
| Terpenoids ,Lignoids M. Betulinic acid , savinin , curcumin ,and niclosamide f ,betulinic acid andsavinin , α-cadinol | inhibitory effects on 3CL ProteaseActivity | -SARS-CoV | (67) | |
| Coumarin | inhibit expression of many chemokinegenes and gene for Nucleoprotein, an influenza structural protein that is aconstituent of vRNPs viral ribonucleoprotein complex important for viralreplication | Influenza Virus | (103) | |
Table: 4
References
- New-type coronavirus causes pneumonia in Wuhan: expert - Xinhua | English.news.cn
- Lai C-C, Shih T-P, Ko W-C, Tang H-J, Hsueh P-R. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 105924.
- Liu S-L, Saif L. Emerging Viruses without Borders: The Wuhan Coronavirus. Viruses. 12(2):130.
- The Elsevier Community [Internet]. Novel Coronavirus Information Center. Elsevier Connect; Elsevier;
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China .
- Wang C, Horby PW, Hayden FG, Gao GF. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet
- National Health Commission of the PRC [WWW Document],
- Ren L-L, Wang Y-M, Wu Z-Q, Xiang Z-C, Guo L, Xu T, et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus causing severe pneumonia in human. Chin Med J (Engl)
- Vellingiri B, Jayaramayya K, Iyer M, Narayanasamy A, Govindasamy V, Giridharan B, et al. COVID-19: A promising cure for the global panic. Sci Total Environ [Internet]. 138277.
- Joseph I. Middle east respiratory syndrome corona virus (MERS CoV): The next steps. J Public Health Policy [Internet]. 36(3):318–323.
- What proportion are asymptomatic p. 19 –19– .
- Mukhtar M, Arshad M, Ahmad M, Pomerantz RJ, Wigdahl B, Parveen Z. Antiviral potentials of medicinal plants. Virus Res. 131(2):111–120.
- Rais-ur-rehman PA, Katoch DC, Siddiqui KM, Khan MA, Jamil S. Unani System of Medicine the science of health and healing. New Delhi: Department of Ayush Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Govt. of India; 39–44 p.
- Mousavizadeh L, Ghasemi S. Genotype and phenotype of COVID-19: Their roles in pathogenesis. J Microbiol Immunol Infect
- Maier HJ, Bickerton E, Britton P, ANALYSTICS CLARIVATE. Coronaviruses: methods and protocols. Berlin: Springer; 1 –1.
- Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A, Dulebohn SC, Di Napoli R. Features, evaluation and treatment coronavirus (COVID-19. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing;
- Organization WH. Coronavirus. WhoInt
- C.D.C. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Adhikari SP, Meng S, Wu Y-J, Mao Y-P, Ye R-X, Wang Q-Z, et al. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) during the early outbreak period: a scoping review. Infect Dis Poverty [Internet]. 9(1).
- Jin Y-H, Cai L, Cheng Z-S, Cheng H, Deng T, Fan Y-P, et al. A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version. Mil Med Res [Internet]. 7(1).
- Protocol on Prevention and Control of COVID-19 . Edition 6.
- C.D.C. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: a model-based analysis. Lancet Infect Dis [Internet]. :1473 –3099 20 30243–7.
- Disease C. COVID-19): Epidemiology, Clinical Spectrum and Implications for the Cardiovascular Clinician
- U. PN| T|. Asymptomatic Tablighi Jamaat cluster spurs research on coronavirus strain in Tamil Nadu |. Apr. 4(22).
- Smallpox A-R, Measles. Muslim Heritage. Kass-Hout T, Zhang X, editors. Biosurveillance: methods and case studies. CRC Press.pg-Xiii;
- Keep your distance – health lessons from the history of pandemicsProphet Muhammad’s teachings regarding pandemicsSingh R. &Adhikari R. Age-structured impact of social distancing on the COVID-19 epidemic in India. Coronavirus N. Situation Summary. Wuhan, ChinaInfectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19 Williams JEBT-AMR. Review of antiviral and immunomodulating properties of plants of the peruvian rainforest with a particular emphasis on una de gato and sangre de grado. 2001 May 8;6(6):567+.
- Shihman Chang R, Yeung HW. Inhibition of growth of human immunodeficiency virus in vitro by crude extracts of Chinese medicinal herbs. Antiviral Res 9(3):163–175.
- Churiyah pongtuluran, B., rofaani e, tarwadi. Antiviral and Immunostimulant Activities of Andrographis paniculata. HAYATI J Biosci. 22(2):67–72.
- Reddy SM, Ravikanth V, Krishnaiah P, Goud T V, Rao TV, Y. A new BIS-Andrographolide Ether fromAndrographis paniculataNees and evaluatin of anti-HIV activity. Nat Prod Res. 19(3):223–230.
- Kurokawa M, Nagasaka K, Hirabayashi T, Uyama S, Sato H, Kageyama T, et al. Efficacy of traditional herbal medicines in combination with acyclovir against herpes simplex virus type 1 infection in vitro and in vivo. Antiviral Res. 27(1–2):19–37.
- Repentis WHOFS. World Health Organization Monographs on Selected Medicinal Plants, vol. 2. Geneva World Heal Organ. 2002;285–99.
- Anti-Infectivity against Herpes Simplex Virus and Selected Microbes and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Compounds Isolated from Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Viruses. 10(7):360.
- May G, Willuhn G. Antiviral effect of aqueous plant extracts in tissue culture. Arzneimittel- Forsch. 28(1):1–7.
- Pourghanbari G, Nili H, Moattari A, Mohammadi A. Antiviral activity of the oseltamivir and Melissa officinalis L . essential oil against avian influenza A virus ( H9N2 ). VirusDisease. 2016;27(2):170–8.
- Astani A, Reichling J, Schnitzler P. Melissa officinalis Extract Inhibits Attachment of Herpes Simplex Virus in vitro. Chemotherapy. 58(1):70–77.
- Alizadeh Behbahani B, Shahidi F. Melissa officinalis Essential Oil: Chemical Compositions, Antioxidant Potential, Total Phenolic Content and Antimicrobial Activity. Nutr Food Sci Res. 6(1):17–25.
- Mazzanti G, Battinelli L, Pompeo C, Serrilli AM, Rossi R, Sauzullo I, et al. Inhibit ory activity of Melissa officinalis L. extract on Herpes simplex virus type 2 replication. Nat Prod Res. 22(16):1433–1440.
- SaiRam M, Ilavazhagan G, Sharma S, Dhanraj S, Suresh B, Parida M, et al. Anti-microbial activity of a new vaginal contraceptive NIM-76 from neem oil (Azadirachta indica. J Ethnopharmacol. 71(3):377–382.
- Faccin-galhardi LC, Aimi K, Ray S, Ray B, Elisa R, Linhares C, et al. The in vitro antiviral property of Azadirachta indica polysaccharides for poliovirus. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;142(1):86–90.
- Bharitkar YP, Bathini S, Ojha D, Ghosh S, Mukherjee H, Kuotsu K, et al. Antibacterial and antiviral evaluation of sulfonoquinovosyldiacylglyceride?: a glycolipid isolated from Azadirachta indica leaves. 2013;
- Badam L, Joshi SP, Bedekar SS. ’In vitro’antiviral activity of neem (Azadirachta indica. A. Juss) leaf extract against group B coxsackieviruses. J Commun Dis. 31(2):79–90.
- Yukawa TA, Kurokawa M, Sato H, Yoshida Y, Kageyama S, Hasegawa T, et al. Prophylactic treatment of cytomegalovirus infection with traditional herbs. Antiviral Res [Internet]. 32(2):63–70.
- El-Mekkawy S, Meselhy MR, Kusumoto IT, Kadota S, Hattori M, Namba T. Inhibitory Effects of Egyptian Folk Medicines on Human Immunodeficiency Virus(HIV) Reverse Transcriptase. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) [Internet]. 43(4):641–648.
- Zhang J, Zhan B, Yao X, Gao Y, Shong J. Antiviral activity of tannin from the pericarp of Punica granatum L. against genital Herpes virus in vitro. Zhongguo Zhong yao za zhi= Zhongguo zhongyao zazhi= China J Chinese Mater medica. 20(9):556–8.
- Hoerhammer L. Flavone concentration of medicinal plants with regard to their spasmolytic action. In: Congr Sci Farm Conf Comun, 21st, Pisa. 1961. p. 578–88.
- A M. Screening of selected plant extracts for in vitro inhibitory activity on HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (HIV-1 RT. Pharmazie. 55:75–77.
- Lee-Huang S, Huang PL, Huang PL, Bourinbaiar AS, Chen HC, Kung HF. Inhibition of the integrase of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 by anti-HIV plant proteins MAP30 and GAP31. Proc Natl Acad Sci [Internet]. 92(19):8818–8822.
- Jiratchariyakul W, Wiwat C, Vongsakul M, Somanabandhu A, Leelamanit W, Fujii I, et al. HIV Inhibitor from Thai Bitter Gourd. Planta Med [Internet]. 67(4):350–353.
- Rehman S, Ashfaq UA, Riaz S, Javed T, Riazuddin S. Antiviral activity of Acacia nilotica against Hepatitis C Virus in liver infected cells. 2011;1–6.
- Raheel R, Aslam MS, Asghar S, Ashraf M. Phytochemical, ethno pharmacological review of Acacia nilotica (desi kikar) and taxo-pharmacology of genus acacia. Indian Res J Pharm Sci. 1:65–72.
- Mishra S, Aeri V, Gaur PK, Jachak SM. Phytochemical, Therapeutic, and Ethnopharmacological Overview for a Traditionally Important Herb:Boerhavia diffusaLinn. Biomed Res Int :1–19.
- Keyaerts E, Vijgen L, Pannecouque C, Van Damme E, Peumans W, Egberink H, et al. Plant lectins are potent inhibitors of coronaviruses by interfering with two targets in the viral replication cycle. Antiviral Res [Internet]. 75(3):179–187.
- Liu Y-T, Chen H-W, Lii C-K, Jhuang J-H, Huang C-S, Li M-L, et al. A Diterpenoid, 14-Deoxy-11, 12-Didehydroandrographolide. Andrographis paniculata Reduces Steatohepatitis Liver Inj Mice Fed a High-Fat High-Cholesterol Diet [Internet]. 12(2):523.
- Liu Z, Xiao X, Wei X, Li J, Yang J, Tan H, et al. Composition and divergence of coronavirus spike proteins and host ACE2 receptors predict potential intermediate hosts of SARS-CoV-2. J Med Virol.
- Fiore C, Eisenhut M, Krausse R, Ragazzi E, Pellati D, Armanini D, et al. Antiviral Effects of Glycyrrhiza species. 2008;148(June 2007):141–8.
- Lilly Ganju SS. Plant Derived Antivirals: A Potential Source of Drug Development. J Virol Antivir Res . 02(02).
- Wen C, Kuo Y, Jan J, Liang P, Wang S, Liu H, et al. Specific Plant Terpenoids and Lignoids Possess Potent Antiviral Activities against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. 2007;4087–95.
- Nassiri Asl M, Hosseinzadeh H. Review of antiviral effects of Glycyrrhiza glabra L. and its active component, Glycyrrhizin. J Med Plants. 2(22):1–12.
- Anagha K, Manasi D, Priya L, Meera M. Scope of Glycyrrhiza glabra (Yashtimadhu) as an Antiviral agent: A Review. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 3(12).
- Woradulayapinij W, Soonthornchareonnon N, Wiwat C. In vitro HIV type 1 reverse transcriptase inhibitory activities of Thai medicinal plants and Canna indica L . rhizomes. 2005;101:84–9.
- Nair R. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibition by Vitex negundo L. leaf extract and quantification of flavonoids in relation to anti-HIV activityJ. Cell Mol Biol. 10:53–59.
- Kothandan S, Swaminathan R. Evaluation of in vitro antiviral activity of Vitex Negundo L., Hyptis suaveolens (L) poit. Decalepis hamiltonii Wight Arn, to Chikungunya virus Asian Pacific J Trop Dis. 4:111– 115.
- Palshetkar A, Pathare N, Jadhav N, Pawar M, Wadhwani A, Kulkarni S. In vitro anti-HIV activity of some Indian medicinal plant extracts. 2020;1–11.
- Moghadamtousi SZ, Kadir HA, Hassandarvish P, Tajik H, Abubakar S, Zandi K. A Review on Antibacterial , Antiviral , and Antifungal Activity of Curcumin. 2014;2014.
- Dao TT, Nguyen PH, Won HK, Kim EH, Park J, Won BY, et al. Curcuminoids from Curcuma longa and their inhibitory activities on influenza A neuraminidases. Food Chem . 134(1):21–28.
- Davis AL, Lewis JR, Cai Y, Powell C, Davis AP, Wilkins JPG, et al. A polyphenolic pigment from black tea. Phytochemistry. 46(8):1397–1402.
- KITAGAWA I, HORI K, MOTOZAWA T, MURAKAMI T, YOSHIKAWA M. Structures of New Acylated Oleanene-Type Triterpene Oligoglycosides, Theasaponins E1 and E2, from the Seeds of Tea Plant, Camellia sinensis (L.) O. KUNTZE Chem Pharm Bull . 46(12):1901–1906.
- Chandel V, Raj S, Rathi B, Kumar D. In silico identification of potent FDA approved drugs against Coronavirus COVID-19 main protease?: A drug repurposing approach. 2020;7(3):166–75.
- Benzekri R, Bouslama L, Papetti A, Hammami M, Smaoui A, Limam F. Anti HSV-2 activity of Peganum harmala (L.) and isolation of the active compound. Microb Pathog [. 114:291–298.
- Álvarez DM, Castillo E, Duarte LF, Arriagada J, Corrales N, Farías MA, et al. Current Antivirals and Novel Botanical Molecules Interfering With Herpes Simplex Virus Infection. 2020;11(February):1–19.
- Barquero AA, Alché LE, Coto CE. Antiviral activity of meliacine on the replication of a thymidine kinase-deficient mutant of Herpes simplex virus type 1 alone and in combination with acyclovir. Int J Antimicrob Agents [Internet]. 9(1):49–55. Available
- Petrera E, Coto CE. Therapeutic effect of meliacine, an antiviral derived fromMelia azedarachL., in mice genital herpetic infection. Phyther Res. 23(12):1771–1777.
- Lipipun V, Kurokawa M, Suttisri R, Taweechotipatr P, Pramyothin P, Hattori M. Efficacy of Thai medicinal plant extracts against herpes simplex virus type 1 infection in vitro and in vivo. Antiviral Res. 60:175–180.
- Lee C-L, Chiang L-C, Cheng L-H, Liaw C-C, Abd El-Razek MH, Chang F-R, et al. Influenza A (H(1)N(1)) Antiviral and Cytotoxic Agents from Ferula assa-foetida. J Nat Prod [Internet]. 72(9):1568–1572.
- Ghannadi A, Fattahian K, Shokoohinia Y, Behbahani M, Shahnoush A. 2014).Anti-viral evaluation of sesquiterpene coumarins from Ferula assa-foetida against HSV-1. Iran J Pharm Res IJPR. 13(2):523.
- Lee JB, Yamagishi C, Hayashi K, Hayashi T. Antiviral and immunostimulating effects of lignin-carbohydrate-protein complexes from Pimpinella anisum. In: Bioscience, biote chnology, and biochemistry. p. 1101242356–1101242356.
- Vimalanathan S, Ignacimuthu S, Hudson JB. Medicinal plants of Tamil Nadu (Southern India) are a rich source of antiviral activities. Pharm Biol. 47(5):422–429.
- Subashini MS, Rajendran P. In vitro screening of anti HBV and anti HIV properties of Gymnema sylvestre R. Br leaves from Kolli Hills, Tamilnadu, India. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci. 4:542–547.
- Chattopadhyay D, Mukherjee H, Bag P. Ethnomedicines in Antiviral Drug Discovery. 2009;
- Hossan S, Fatima A, Rahmatullah M, Jin T, Veeranoot K, Wiart C. Antiviral activity of Embelia ribes Burm . f . against influenza virus in vitro. Arch Virol 2018;(0123456789).
- Parida MM, Upadhyay C, Pandya G, Jana AM. Inhibitory potential of neem ( Azadirachta indica Juss ) leaves on Dengue virus type-2 replication. 2002;79:273–8.
- Ashraf A, Ashraf MM, Rafiqe A, Aslam B. In vivo antiviral potential of Glycyrrhiza glabra extract against Newcastle In vivo antiviral potential of Glycyrrhiza glabra extract against Newcastle disease virus. 2017;(April).
- Liou C-J, Cheng C-Y, Yeh K-W, Wu Y-H, Huang W-C. Protective Effects of Casticin From Vitex trifolia Alleviate Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in a Murine Asthma Model. Front Pharmacol 9.
- Calabrese C, Berman SH, Babish JG, Ma X, Shinto L, Dorr M, et al. A phase I trial of andrographolide in HIV positive patients and normal volunteers. Phyther Res. 14(5):333–338.
- Polyak SJ, Ferenci P, Pawlotsky JM. Hepatoprotective and antiviral functions of silymarin components in hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology. 57(3):1262–1271.
- Qi F, Wang Z, Cai P, Zhao L, Gao J, Kokudo N, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine and related active compounds: a review of their role on hepatitis B virus infection. Drug Discov Ther. 7(6):212–224.
- Wei L, Li Z, Chen B. Clinical study on treatment of infantile rotaviral enteritis with Psidium guajava L. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi Chinese J Integr Tradit West Med. 20(12):893–895.
- Vaidya AB, Antarkar DS, Doshi JC, Bhatt AD, Ramesh V V, Vora P V, et al. Picrorhiza kurroa ( Kutaki ) Royle ex Benth as a hepatoprotective agent--experimental & clinical studies . 2020;(4):5–8.
- Seniya C, Shrivastava S, Singh SK, Khan GJ. Analyzing the interaction of a herbal compound Andrographolide from Andrographis paniculata as a folklore against swine flu (H1N1. Asian Pacific J Trop Dis [Internet]. 4:624– 630.
- Gangarapu K, P S, K K, KM K, D RK, MS S, et al. In Silico Computational Screening of Kabasura Kudineer - Official Siddha Formulation and JACOM - Novel Herbal Coded Formulation Against SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein. SSRN Electron J
- Ashfaq UA, Jalil A, Qamar MT. Antiviral phytochemicals identification fromAzadirachta indicaleaves against HCV NS3 protease: an in silico approach. Nat Prod Res [Internet]. 30(16):1866–1869. Available from:
- Chandel V, Raj S, Rathi B, Kumar D. In Silico Identification of PotentCOVID-19Main Protease Inhibitors from FDA Approved Antivira Compounds and ActivePhytochemicals through Molecular Docking: A Drug Repurposing Approach.
- Mishra S, Pandey A, Manvati S. Heliyon Coumarin?: An emerging antiviral agent. Heliyon [Internet]. 2020;6(November 2019):e03217.

Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences